Sebi was established in 1988 by the Government of India and the power was given on 30th Jan 1992.
Objective
- prevent trading malpractice
- protect rights and interest of investors
- regulate and develop a code of conduct
- regulate Stock Exchange
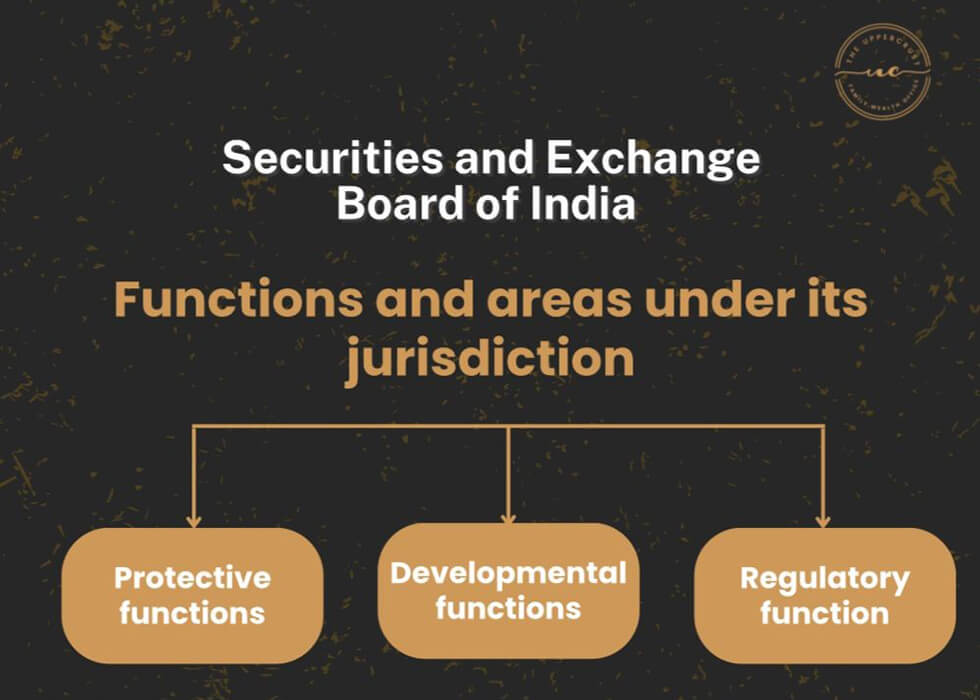
Functions of SEBI
1. Protective functions
- Prohibits fraudulent and unfair trade practice
- Promotion of Fair practice and code of conduct
- Undertaking steps for investor protection
- Controlling insider trading and imposing penalties and search malpractices
2. Developmental functions
- Ensuring training of intermediaries of stock market
- Protecting interest of investors
- Facilitating flexibility in working of capital market
3. Regulatory function
- Registration and regulation of brokers and sub brokers
- Registration of collective investment scheme and mutual fund
- Conducting enquiries and audit of Stock Exchange and intermediaries
- Regulation of portfolio exchange underwriter and dealing in Stock Exchange
- Regulation to takeover bid by the competitors
This is a little insight to what SEBI does and what areas are under its jurisdiction.
Why was SEBI established?
With the growth in the dealings of stock markets, a lot of malpractices also started in stock markets such as price rigging, ‘unofficial premium’ on new issues, and delay in delivery of shares, violation of rules and regulations of stock exchange and listing requirements. Due to these malpractices the customers started losing confidence and faith in the stock exchange. So, the government of India decided to set up an agency or regulatory body known as Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
SEBI went from being a toothless tiger to strong as a lion after the government saw the real need to bring regulatory intervention in the capital market following events in the 1990s. SEBI was tasked with being a watchdog for the capital market in India. Over the years it has made the Indian capital market a much safer place for investors to participate. It has surely increased investors’ trust in Indian markets by taking firm actions on the fraudulent activity by any and all participants of capital markets from investors to stock exchanges. Building the trust in the capital market for HNIs to Retail investors is a very crucial task for free flow and working of capital in India.
List of effective changes Introduced by SEBI in capital market
- T+2 trading settlement system.
- Dematerialization of share certificates (1999).
- Banned entry loads for mutual fund schemes in 2009
- The task of giving approvals to FII registrations was handed over to SEBI in 2003. In order to discourage FII investments made through P-notes, Securities and Exchange Board of India has imposed sufficient checks and balances to avoid the flow of black money into the Indian markets.
- Strict vigil on usage of IPO 1ssue proceeds, greater disclosure by companies and their bankers and allotment of a minimum number of shares to retail investors.
- SEBI has also introduced e-IP0 procedure for electronic bidding in public offers to help investors bid for shares in a cost-effective manner.
- In 1996-97, Securities and Exchange Board of India directed all exchanges to fix the daily price band at 10% and a weekly overall limit of 25% to curb undesirable volatility. To bring about a coordinated trading halt in all equity and derivatives markets nationwide, Securities and Exchange Board of India introduced an index-based circuit breaker system applicable at 10%, 15% and 20% movement either way.
- Securities and Exchange Board of India has a web-based centralized grievance redress system called SEBI Complaints Redress System SCORES for assisting investors to lodge their complaints in a structured way.
- NB: International Organization of Securities Commissions- IOSCO under its Financial Sector Assessment Program -FSAP acknowledged that the comprehensive risk management framework prescribed by SEBI is one of the pillars of the Indian securities settlement system.
- Securities and Exchange Board of India distinguishes itself from other regulators in India as it is a financially independent regulator with its own sources of revenue.
Over the years SEBI as a regulator has issued numerous regulations to create checks and balances over all the participants of the capital market. These regulations on: Merchant bankers, Stock brokers, Debenture trustees, Share transfer agent, Bank to an issue, Custodian, Mutual fund, Collective investment scheme, Credit rating agencies, Foreign venture capital investors, Associated person to securities market, Intermediaries, Securitised debt instrument, Alternate investment funds, Investment advisor, Infrastructure investment trust, Real estate investment trust, Research analyst, Stock exchange and clearing corporation, Foreign portfolio investors, Portfolio manager, Underwriter, Vault manager.
SEBI has also issued regulations regarding the functioning of a listed entity and its function. These are as follows:
- Procedure for board meeting
- Employee services
- Key your customer (KYC)
- Listing obligation and disclosure requirements
- Buy-back securities
- Issue of capital and disclosure requirement
- Settlement procedure
- Delisting of equity shares
- Issue of non-convertible securities
All these regulations have a reason and a story behind it, to protect the market participants from illegal and fraudulent activities. All the regulations are welcomed by each and every party.
Why should SEBI regulation be welcomed?
The whole system works on trust between parties. These regulations are from a common sense approach to effective and efficient function of the capital market and which return increases confidence in the investors. Without regulations there have been instances which destroyed investors’ wealth. We can see what has happened to the cryptocurrency market in 2022 due to no regulations in the market. It has caused chaos and welcomed fraudulent schemes blowing up and destroying investors capital and which has discouraged people from getting into the market again. SEBI has welcomed new products and made rules and regulations according to the main function of SEBI in the center to encourage innovation in financial products as well as protecting investors at large.
Now retail investors have access to a lot of products which were not in reach due to barriers to entry. Due to SEBIs intervention resulted in access to those products at the same time making it safer for the retail investors.