Every person has some financial goals like retirement, medical plan, child’s education, travelling, getting a new house, car, etc. Please refer to the below image:
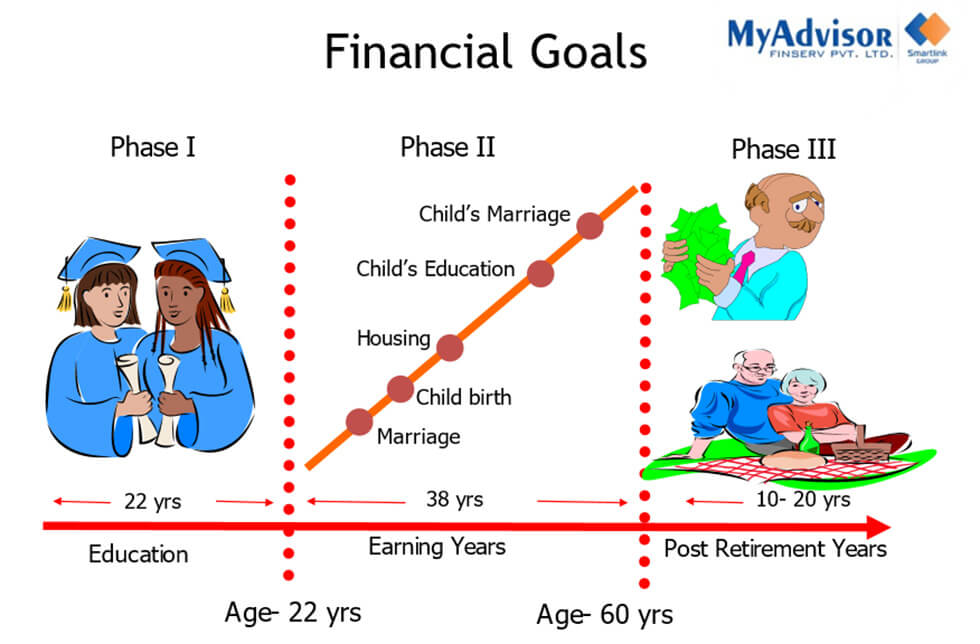
As can be seen above, every individual has limited earning life (Phase II) and has financial goals to achieve from birth till the end of life.
Every person has a surplus income during his/her earning life and looks for investment options where he/she can park his money.
Among various investment options, Fixed Income options were the most popular ones in the last 50 years. FD, Bonds, Debentures, LIC, PPF or Post Office saving schemes are a part of the Fixed Income asset class. Capital protection and Fixed Income is the most loved feature enjoyed by most Indian investors till now.
Post Liberalization of the Indian economy in 1991, things started changing. After 1991, the Economy which was in the doldrums started to take baby steps. The speed of improvement was slow from 1991 till 2003. Post that liberalization started showing its results and the Indian economy started showing visible improvements. The effect of this was a significant reduction in Interest rate. On one hand it helped many Indian entrepreneurs to raise cheap capital for their ventures, but on the other hand reduced Fixed Interest to the Savers.
India’s long term Inflation average is around 6.5%. We know that each asset class returns must beat Inflation in order to remain attractive in a long run. As can be seen in the image below, post 2003 the Fixed Interest returns diminished and started kissing the inflation or lately now have even started to even underperform. Long term returns of different investment avenues above the dotted line of average inflation can be observed below.
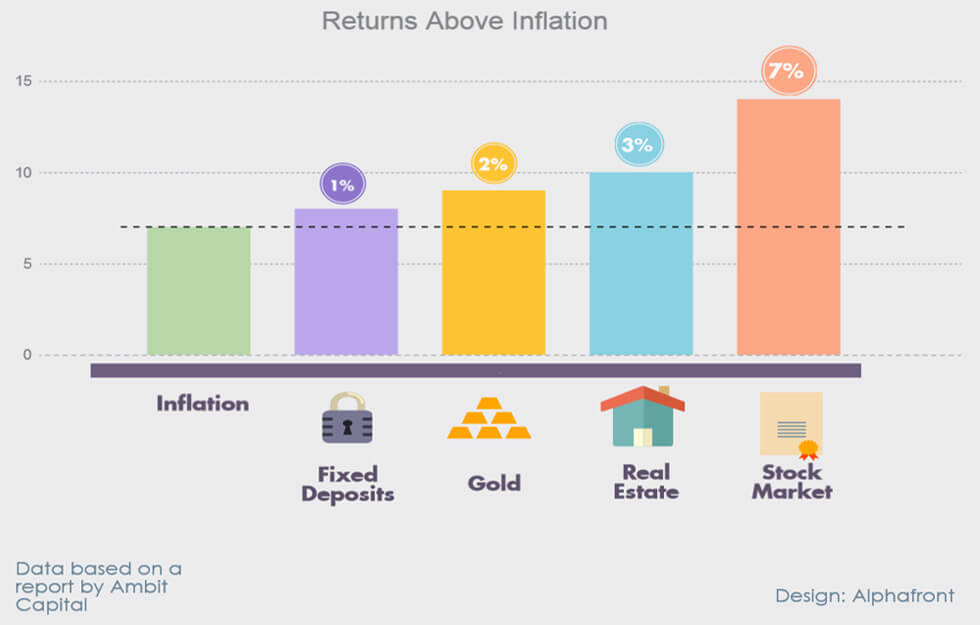
In the situation where most loved Fixed Income products started underperforming Inflation for a long time, the Investors had no option but to look for other investment classes at the cost of increased risk. Gold & Real Estate offered a small overperformance over Inflation.
Gold & Real Estate offered a small over performance over Inflation. But at the same time had some disadvantages such as low liquidity, physical nature & a large ticket size with storage or maintenance cost.
Equity / Stock Markets, on the other hand, had a significant overperformance compared to Inflation but it is a very volatile asset class as per the popular perception of a common man. We can see the typical returns below:
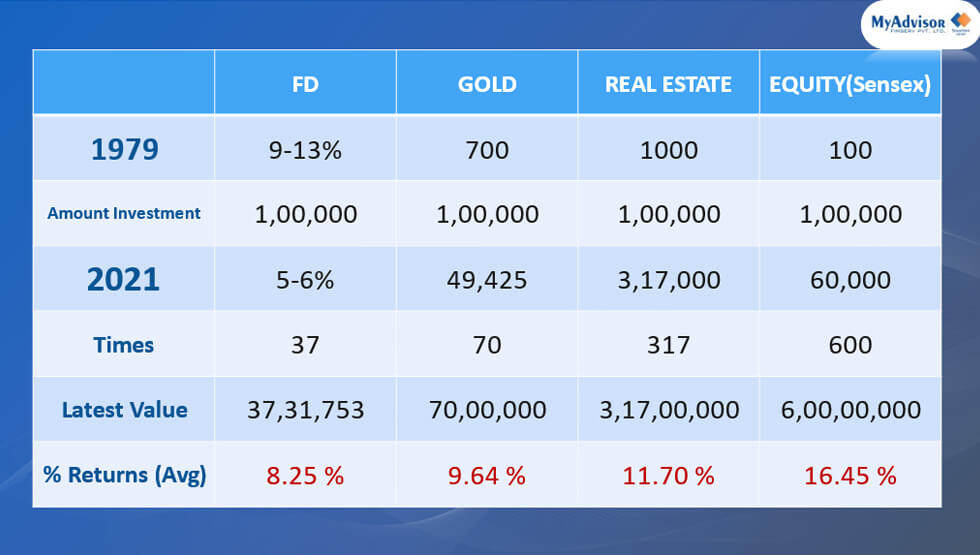
On a closer look & data crunching, the Equity asset class in the short term looked to be extremely volatile & unreliable, was not that volatile or unreliable in horizons of 5 years or above. So, investors who were ready to park their surplus funds for a long term started understanding this asset class.
Also, the introduction of managed products in the Equity asset class such as Mutual Funds or PMS during the period 1996 to 2000 allowed an entry of common investors to park their surplus money. By 2010, many investors and analysts had understood that Mutual Funds were a less volatile & professionally managed version of Equity investment that gave significantly higher returns compared to all other asset classes in the long run.
Investors realized and adjusted to the nature of equity over some time. They realized that equity has the following features:
- Equity can significantly beat Inflation in the long term
- Equity provides higher liquidity compared to most other asset class
- Equity is the most efficient asset class in India
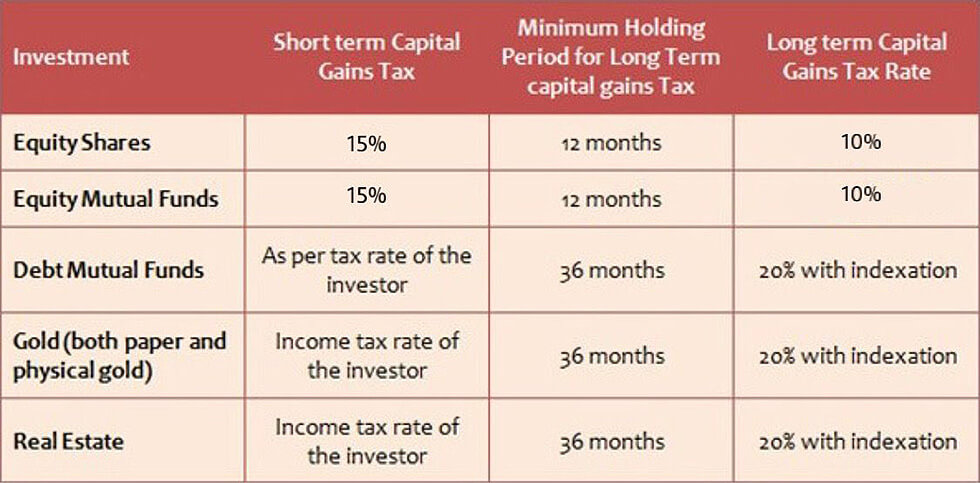
But it also must be taken into consideration that:
- Different asset classes Outperform / Underperform each other in different market cycles.
- .Investors also have requirements for their surplus in the short term
The above facts also warrant that a proper Asset Allocation is required when it comes to parking your total investible surplus. The following must be considered while doing Asset Allocation:
- Risks & Rewards are interrelated i.e. Higher returns, higher the risk
- Asset Allocation protects from the vagaries of the market
- Situations in life can be unpredictable and liquidity is extremely important
- Asset allocation is different for different person
Portfolio adjustment as per risk bearing capability
Younger people who have time for an investment to grow and compound should have a major portion of their portfolio in equities (say 60-65%). While risk-averse and elder Investors should have more of debt, liquid assets and lesser equity (less than 30%) in their portfolio.
Key Takeaways
- Invest in equity to gain higher returns.
- Stay invested in equity for a longer period.
- For short term investments, prefer FDs, Bonds and Liquid assets.
- The portfolio should be well-diversified and at the same time have assets that can meet financial goals.
- Equity investment should also consider the risk-taking ability of the investor.
The author is the Director – Of private Wealth at UpperCrust Wealth Pvt. Ltd. With his distinct style and belief in picking. “Return Generating Strategies” which is flexible to suit different market moods and over 25 years of experience in leading investment strategy/research team, establishing effective and well-organized investment processes, quantitative and qualitative portfolio allocation and manage client relationships in financial markets, he has worked with some of the leading names in the financial markets.

